Signs of Retinal Damage: When to See a Retinal Specialist
Retinal damage can lead to serious vision problems if not addressed promptly. Understanding the signs and symptoms is crucial for anyone concerned about their eye health. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of retinal damage, when to seek help from a specialist, and treatment options available.
Understanding Retinal Damage
The retina is a thin layer of tissue located at the back of the eye, converting light into neural signals and sending them to the brain. Damage to this fragile layer can lead to significant vision impairment or even blindness.
What is the Retina?
The retina consists of photoreceptor cells called rods and cones, which allow us to perceive light and color. These cells are highly sensitive and play a vital role in our visual acuity. The retina also includes other important structures, including the macula, responsible for sharp central vision.
Retinal health is critical not only for good eyesight but also for overall well-being. Damage to the retina can disrupt the entire visual process, leading to distorted vision or dark spots in the field of view. The retina’s ability to adapt to varying light conditions is also essential for activities such as driving at night or reading in dim light. Any compromise to this system can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life, making regular eye examinations crucial for early detection of potential issues.
Common Causes of Retinal Damage
There are several factors that can lead to retinal damage, each requiring different forms of treatment. The most common causes include:
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
- Retinal detachment
- Injury to the eye
- Genetic disorders
Diabetic retinopathy is especially prevalent among individuals with uncontrolled diabetes, where high blood sugar levels can cause damage to the blood vessels in the retina. Similarly, AMD affects older adults and can lead to severe vision loss if untreated. The risk factors for these conditions often overlap, with lifestyle choices such as diet, exercise, and smoking playing significant roles in their development.
Recognizing these causes is essential for prevention and early intervention, helping to safeguard vision over time. Regular eye check-ups can help detect early signs of retinal damage, allowing for timely treatment options such as laser therapy or injections that can stabilize or even improve vision. Additionally, advancements in medical technology, including imaging techniques like optical coherence tomography (OCT), have revolutionized the way retinal diseases are diagnosed and monitored, providing a clearer picture of retinal health and enabling more personalized treatment plans.
Identifying the Signs of Retinal Damage
Being aware of the symptoms of retinal damage can empower individuals to seek timely treatment. Early detection can significantly improve outcomes and preserve vision.
Early Symptoms to Watch Out For
Initially, retinal damage may manifest through subtle signs that can easily be overlooked. Common early symptoms include:
- Blurry or distorted vision
- Difficulty seeing in low light
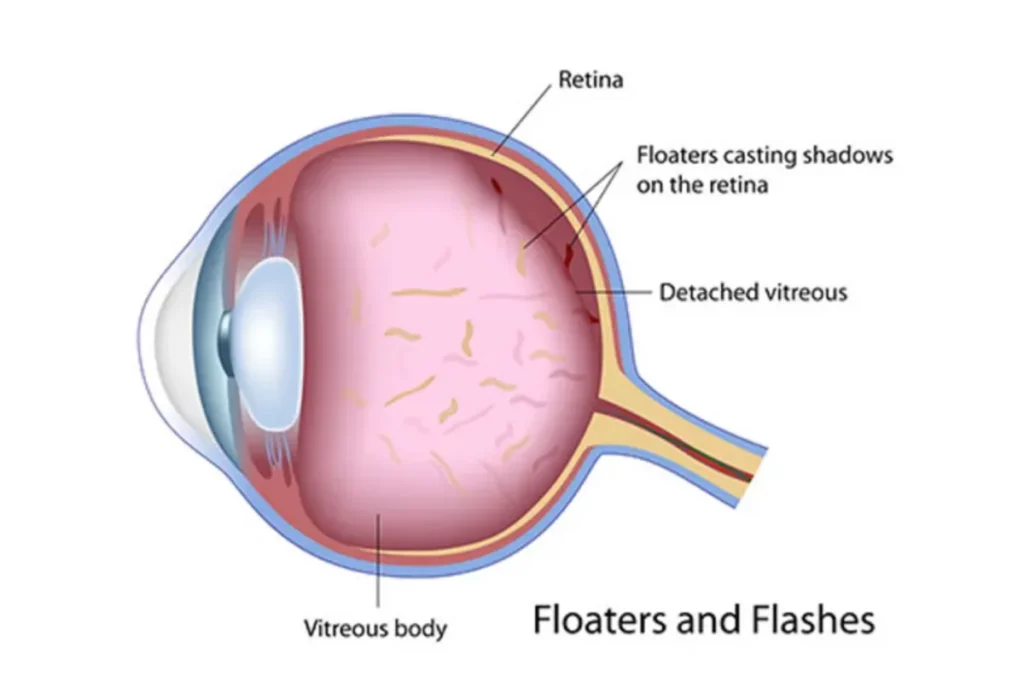
- Sudden appearance of floaters
- Light flashes in your vision
If you begin to notice these changes, it is essential to consult an eye care professional as soon as possible. Early diagnosis can prevent further deterioration of your eyesight. It is also important to consider that some individuals may experience these symptoms differently, and the severity can vary widely. For instance, floaters may appear as small specks or cobweb-like strands that drift across your field of vision, while light flashes may feel like brief bursts of light that can be disconcerting and alarming.
Advanced Indicators of Retinal Damage
As retinal damage symptoms may become more pronounced. Advanced indicators include:
- Loss of central vision
- Dark or empty areas in your visual field
- Severe vision loss that affects daily activities
These advanced signs are serious and typically indicate significant retinal damage. Immediate consultation with a retinal specialist will be crucial in these situations. In some cases, patients may find themselves struggling with tasks that were once routine, such as reading or recognizing faces, which can lead to frustration and emotional distress. Understanding these advanced symptoms is vital, as they can serve as a wake-up call for individuals who may have previously dismissed their early warning signs. Moreover, the psychological impact of vision loss should not be underestimated; many individuals may experience anxiety or depression as they navigate the challenges of adapting to their changing eyesight.
The Role of a Retinal Specialist
A retinal specialist is a medical doctor who focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of diseases and disorders affecting the retina and vitreous humor. Their expertise is vital in addressing complex retinal issues that general practitioners may not be equipped to handle.
Who is a Retinal Specialist?
Retinal specialists typically undergo extensive training, including medical school, a residency in ophthalmology, and additional fellowship training in retina care. This specialized education equips them with the knowledge and skills to diagnose and treat a variety of retinal conditions.
Most retinal specialists use advanced imaging technology, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fluorescein angiography, to visualize the retina in detail and develop a comprehensive treatment plan. These imaging techniques allow specialists to detect subtle changes in the retina that may indicate early stages of diseases such as diabetic retinopathy or age-related macular degeneration, enabling timely intervention.
The Importance of Specialized Eye Care
Consulting a retinal specialist is pivotal for managing retinal damage effectively. They can provide tailored treatment plans based on individual needs, leading to better outcomes. Specialized care can also involve clinical trials or innovative therapies not available at general practices. For instance, retinal specialists may offer cutting-edge treatments like anti-VEGF injections or laser photocoagulation, which can significantly slow the progression of certain retinal diseases.
By addressing retinal issues promptly with a specialist, patients can have a much higher chance of preserving their vision and preventing permanent damage. Furthermore, retinal specialists often collaborate with other healthcare providers, including endocrinologists and primary care physicians, to ensure a comprehensive approach to a patient’s overall health, particularly in cases where systemic conditions like diabetes or hypertension are involved. This multidisciplinary strategy not only enhances the management of retinal diseases but also supports the patient’s overall well-being, emphasizing the interconnectedness of systemic health and eye care.
When to Consult a Retinal Specialist
Determining when to see a retinal specialist can be challenging for many patients. However, understanding key indicators can guide you in seeking the right care.
Timing and Frequency of Eye Examinations
Individuals with risk factors for retinal diseases, such as diabetes or a family history of eye disorders, should have regular eye examinations. It is generally recommended to have a comprehensive eye exam at least once a year. However, those at higher risk may require more frequent visits. Early detection is crucial, as many retinal conditions can progress without noticeable symptoms until significant damage has occurred.
Once a retinal condition has been diagnosed, follow-up appointments will be essential to monitor any changes and adjust treatment as necessary. These visits allow the specialist to track the effectiveness of prescribed therapies and make timely decisions about further interventions, which may include laser treatments or injections that can help preserve vision.
Urgent Situations Requiring Immediate Attention
Certain symptoms should not be ignored and require immediate consultation with a retinal specialist. These situations include:
- Sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes
- Seeing multiple flashes of light
- Massive increases in floaters or a curtain-like shadow across the vision
These symptoms could indicate serious conditions such as retinal detachment or severe bleeding, both needing prompt medical intervention. Additionally, patients should be aware that other warning signs, such as persistent blurred vision or difficulty seeing at night, can also signify underlying retinal issues that warrant further investigation. Being proactive about eye health is essential, especially for those with pre-existing conditions or a family history of retinal diseases.
Furthermore, it is important to recognize that some retinal conditions may develop gradually, leading to subtle changes in vision that can be easily overlooked. Regular communication with your eye care provider about any new or unusual visual experiences can help ensure that any potential issues are addressed early. Keeping a record of any changes in your vision can also be beneficial during consultations, as it provides the specialist with valuable information to aid in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Treatment Options for Retinal Damage
Once a diagnosis has been made, retinal specialists can offer a variety of treatment options tailored to the specific condition and severity of the damage.
Non-Surgical Interventions
Non-surgical treatments might include laser therapy, injectable medications, or photodynamic therapy. These options aim to stabilize or improve vision without the need for invasive procedures.
For instance, laser photocoagulation is often used to seal leaking blood vessels in cases of diabetic retinopathy, reducing the risk of vision loss. Another non-surgical option is the use of anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) injections, which help to reduce swelling and prevent the growth of abnormal blood vessels in conditions like age-related macular degeneration. These injections can significantly improve visual acuity and quality of life for many patients.
Surgical Procedures for Retinal Repair
In cases of more severe retinal damage, surgical intervention may be needed. Procedures like vitrectomy or retinal detachment surgery can restore or preserve vision. During vitrectomy, the surgeon removes the vitreous gel that may be pulling on the retina, alleviating tension and allowing for better healing.
Surgery can be critical in preventing further loss of vision and, in some cases, even restoring lost vision. It’s essential to discuss treatment options thoroughly with your retinal specialist to determine the most appropriate path forward. Additionally, advancements in surgical techniques, such as the use of minimally invasive tools and enhanced imaging technologies, have greatly improved the success rates of these procedures. Patients can expect a more comfortable recovery process with reduced risks of complications, making it easier to return to their daily lives.
Furthermore, post-operative care is a crucial aspect of the treatment journey. Regular follow-up appointments allow the specialist to monitor healing and address any concerns that may arise. Patients may also be advised on lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and protective eyewear, to support overall retinal health and prevent future issues. Engaging in a proactive approach to eye care can empower patients to take charge of their vision health and make informed decisions about their treatment options.
See Also: Retinal detachment treatments: what to expect and when to seek help.